Challenge & Context
The beaches of Montevideo are loved by locals and visitors alike and provide an ideal situation to run a data-driven smart city project aimed at improving the beach-going experience. Montevideo has 18 beaches stretching along more than 15km of coastline and more than 30 lifeguard stations. By integrating cutting-edge FIWARE technology and open data, a unified system has been created for beach visitors to access real-time information on weather, crowds, beach and safety conditions.
Solution
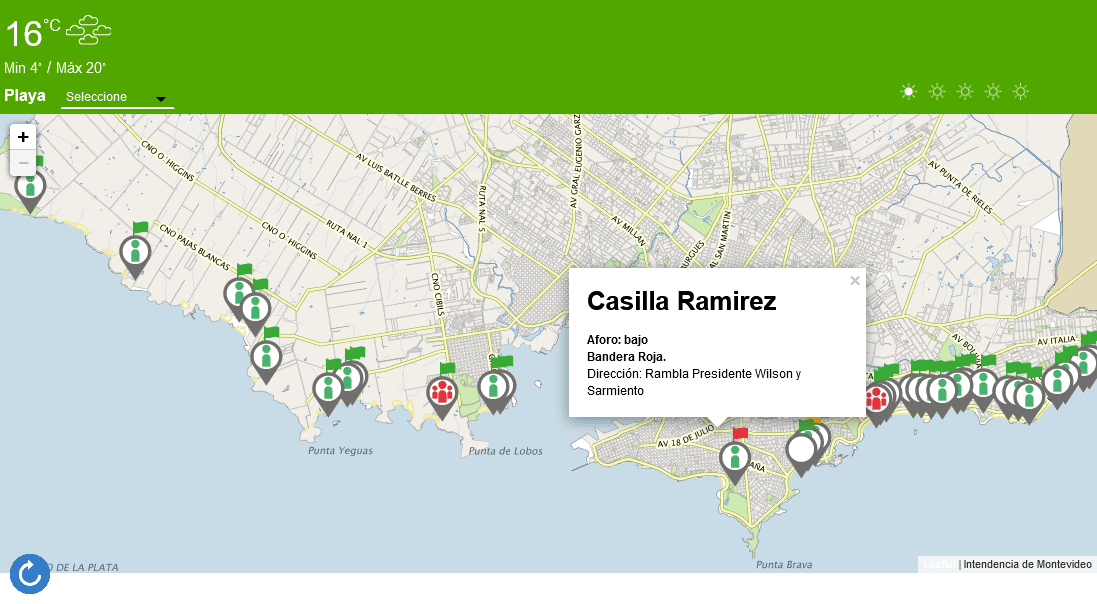
A system, which runs primarily during the summer season has been integrated with the FIWARE platform, specifically the Context Broker, where data is collected from each lifeguard station. Drones act as another collection point, monitoring the beaches for population so as to avoid overcrowding. Data available to users of the platform include weather conditions, a real-time flag status for each of the 18 beaches along with current capacity levels.
Figure 1 . User Interface – Beach visualization data points
The user interface consists of a GIS (Geographic Information System) web application incorporated within the beach page of the municipality. This information not only consists of the data received from the lifeguard boxes but also adds the values of UV index, temperature and weather. UV index data is obtained from the municipality’s own radiometers (connected by FIWARE IOT agents) while weather data is obtained through an interconnection with the INUMET platform (INstituto Uruguayo de METeorología is the official state meteorological agent). In this way, beach users have real time information on the state of each beach in Montevideo.
How it works
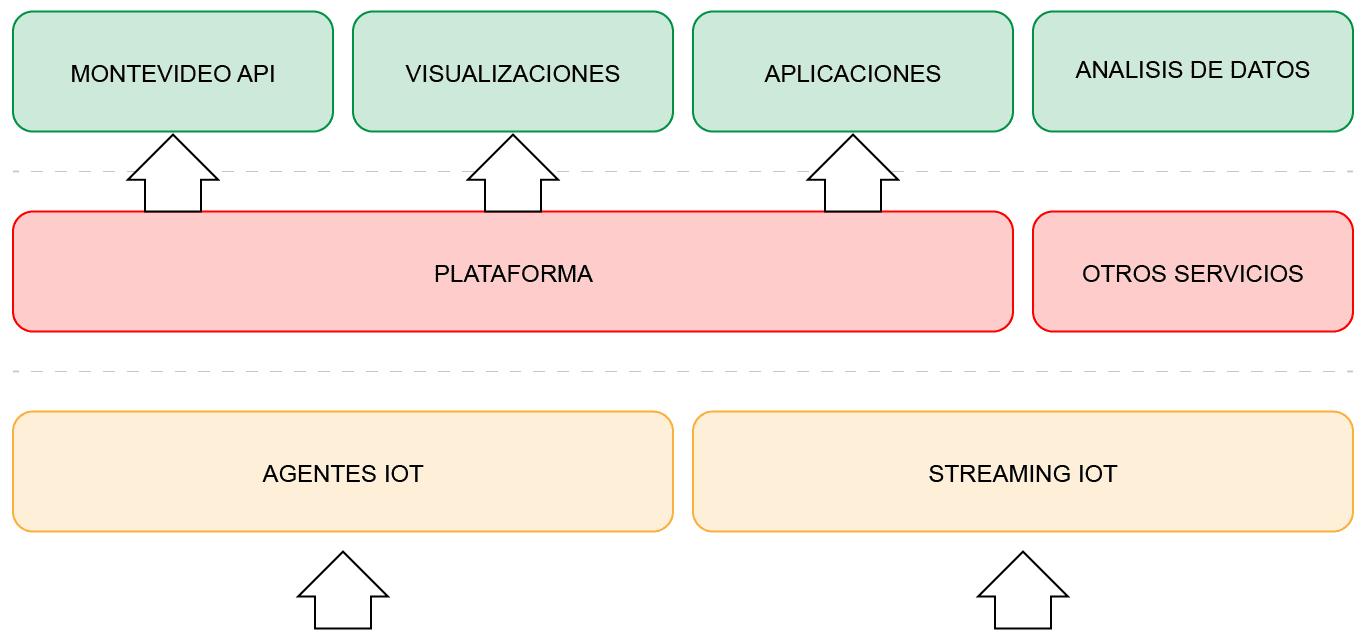
The first installations with the Context Broker sitting in the center of the solution already contained information on UV radiation measured by sensors and weather status/forecast through a B2B integration with the country’s official meteorological institute. In addition, a data model was generated incorporating the lifeguard boxes as entities in the FIWARE Context Broker and a management system was implemented using different sources to update this information. The management system is used by the main actors involved: the technicians who monitor the water quality and the lifeguards who define the bathing flag and the beach capacity. A web app has also been created (mobile and on the IM’s website) which consults the status of these different entities in the Context Broker through sources and provides the information visually on a map. One last aspect to highlight is that the services used in this solution are available through the Open Services portal.
Figure 2 . Solution Architecture Diagram
Benefits & Impact
Both locals and visitors of Montevideo have access to real-time data allowing people to make informed decisions when visiting the beaches. This can aid in distributing the beach goers more evenly across the 18 beaches avoiding overcrowding. Any photos taken by drones once they are processed by analytics are not stored on servers in order to preserve privacy.
The FIWARE platform is connected to an API Manager providing services to the general public. In this case, a REST API exposes the same data which is displayed in the application. Although this is available to the general public, it is most frequently used by people in academics and business, for research and applications development. Today it is used, among others, for example, by DINAMA (National Directorate of Environment) to access real-time data from the beaches of Montevideo.
Added value through FIWARE
Montevideo has had the FIWARE platform installed in its infrastructure since 2018. The platform sits as the fundamental pillar when connecting data from different devices such as radiometers, weather stations (connected by FIWARE IOT agents) and data interconnected with the INUMET platform (the official state agent of meteorology). It has also been key to display the information through this application and the connection with the API Manager.
Finally, to highlight the benefits of having a platform that offers open services to citizens, companies, other civil society organizations or academia, they promote an ecosystem that enables the generation of products adding tangible value.
Next Steps
Montevideo is currently working on a project to expose open data to citizens through Ckan connected to the FIWARE platform. This will enable, in addition to having real-time services — through FIWARE and the API Manager — to expose another set of data in open formats, generating a single place to publish and expose this type of institutional information.